Introduction to DevOps
You will read an introduction to the concept of DevOps to understand the origin and the stakes of this philosophy.
What is DevOps ?
Introduction
DevOps is an approach that brings together the two main functions of a company’s Information Systems Department:
- The development team (Dev)
- The system operations team (Ops)
The DevOps movement was born in 2007 following the dissatisfaction of the system administration staff regarding Agile methods. Indeed, for several years, these methods have privileged the development part while neglecting the production system part, which created technical difficulties or very complex processes regarding the deployment and maintenance of services.
DevOps and Agile methods
Agile methods are software development methods that place the customer at the center of the project. The development team creates a minimal version of the application and then adds new features through an iterative process that includes unit testing, integration testing and code review/improvement.
These iterations allow for regular feedback from the customer to the development team on the functionalities brought to the application and therefore allow the customer to better follow the progress of the project compared to a traditional method and to avoid the tunnel effect as much as possible.
DevOps allows a better collaboration between the technical teams, the quality department and the system operation team in order to better integrate and deliver the different functionalities of a software in a production environment.
DevOps Practices
To avoid any ambiguity, it is necessary to define and differentiate the main axes of a continuous software development process.
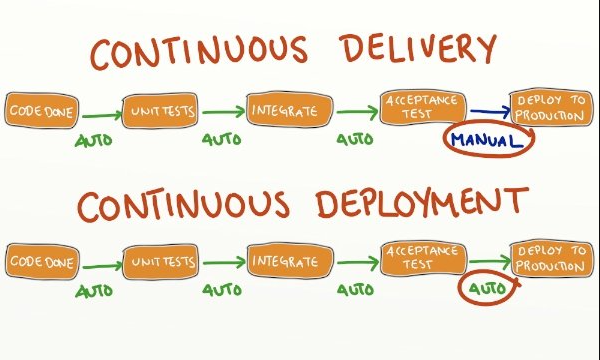
The principle of continuous delivery is that each modification of the code must lead to a new version integrating a new major capability or a set of small modifications.
This principle is often confused with continuous deployment. It is the last step of the process and aims at deploying each new version in one or several environments of recipe or production in an automatic way.
The Stakes
The implementation of CI / CD can allow software developers to save a considerable amount of time, but also to have a stricter and more regular quality control during development.
The implementation of a chain of CI / CD would then allow a net improvement of the quality of the applications by the passage of the tests of reliable quality requirements while unloading the developers of these tasks.
It could also fluidize and balance the workload between developers and network administrators, especially during deployments in the acceptance and production environment. Since most tasks are automated, teams could more easily delegate certain tasks while guaranteeing a favorable result.
On the other hand, the implementation of non-adapted solutions could lead to too many changes in the development processes, which could cause a poor knowledge of the quality requirements among the employees and slow down the development of the product.
The outcome of a project like this would bring a significant gain in productivity and a clear improvement in the profitability of software projects. This would also allow a significant reduction in the number of post-deployment incidents thanks to a reduction in human factor errors during the creation of a version to be delivered (forgotten elements, minor bugs, etc.) or during the application of patches in the acceptance environment.
Conclusion
To recap, we can say that despite the complexity of the job, DevOps requires technological knowledge, but above all, a certain reasoning based on automation and on a sustained technological watch.
However, it’s helping software development in a fantastic way. It’s bridging the gap between developers’ need for change and operations’ resist to change and thus creates a smooth path for Continuous Development and Continuous Integration.